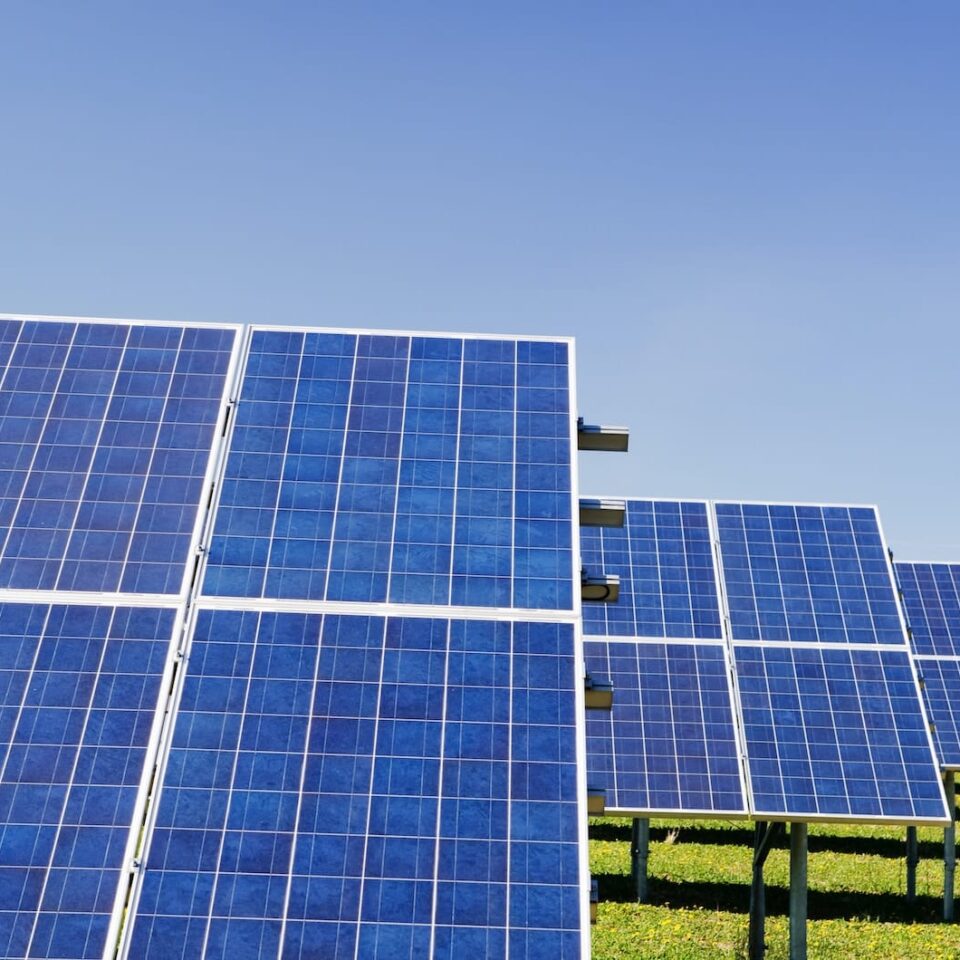
The industry offers different types of solar panels. Each has benefits and drawbacks. However, let’s first understand what solar panels are and how they operate before delving into the wide varieties of solar panels.
Do you intend to switch to solar power? Although purchasing a solar panel for your home may seem complicated, it is comparable to buying a new phone.
Before purchasing a phone or laptop, we conduct extensive research. Buying a solar power plant follows the same logic.
The answer depends on where you live, whether or not you want to install a system at home, and how much power you need.
Solar energy has become increasingly important over the last decade. In 2016 alone, global demand for solar electricity grew by 30%.
Additionally, this growth is expected to continue, especially since renewable sources such as wind and solar are becoming cheaper and more efficient.
Some different types of solar panels are listed below:
1. Polycrystalline Silicon Solar Panel
As shown in the diagram below, polycrystalline silicon solar cells are used to create polycrystalline silicon solar panels.
These cells transform solar energy into electrical energy, making them true energy converters.
Furthermore, a solar panel can have any number of solar cells, although the most common numbers are 60, 72, and 96.
Solar cells and solar panels are made of polycrystalline silicon. A solar panel will produce more energy and expand in size as more cells are added.
The less expensive polycrystalline silicon is used to create these solar cells. They are therefore less costly than monocrystalline.
High purity crystalline silicon with uneven grain boundaries is known as polycrystalline silicon. The structure’s irregularities cause Nonhomogeneity in the material.
Additionally, Crystal characteristics, thermal properties, and electrical properties change over the material.
As a result, electrical charges encounter resistance, which lowers the solar cells’ efficiency. Polycrystalline solar panels are therefore less expensive but less effective.
Polycrystalline silicon solar panels have an efficiency range of 15% to 18%. For more recent panels, it could go up to 19%.
2. Monocrystalline Solar Panels
Monocrystalline Solar Panels are also one of the different types of solar panels. Furthermore, Monocrystalline solar panels are the most prevalent solar panel types available on the market.
These solar panels are fantastic solutions when you need something dependable and capable of giving you clean energy.
Overall, the solar panels’ energy-gathering method is quite effective. Among the solar panel kinds that are commercially available, it has the highest efficiency rate.
However, these solar panels can convert 20% of the energy they absorb into electricity. Recent monocrystalline solar panels even can outperform that 20% figure.
With more advanced technology, these solar panels are becoming more efficient. Additionally, this type of solar panel is typically the most effective.
3. Thin-film Solar Panel
Compared to the first two, thin-film solar panels are considerably different and somewhat challenging to explain. On a substrate, thin films of other photovoltaic materials are deposited to create them.
Thin-film solar cells come in various forms, but three of them have gained widespread acceptance.
And they are amorphous solar cells, copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS), and cadmium telluride (CdTe) solar cells. Additionally, the first of the three, CdTe, is more prevalent than the other two.
Thin-film solar cells are exactly that—they are exceedingly thin. From nanometers to micrometers is the range of their thickness. Furthermore, they are exceptionally light and flexible due to their extreme slenderness.
Additionally, there are no standard sizes for this kind of solar panel. The panels come in a wide range of variants on the market.
The availability of rigid, thin-film panels is another point to be aware of. Yes, a stiff solar panel can be created by sandwiching the thin film between two pieces of glass. But in such a scenario, it would also lose its weightlessness in addition to its flexibility.
4. Amorphous Silicon Solar Cell
Due to their widespread application in various products, amorphous silicon solar panels are prevalent.
Modern products like solar-powered charging ports are becoming more widespread. Solar-powered devices are now widely used by people, and in the years to come, they are likely to become even more prevalent.
Additionally, these devices are typically powered by amorphous silicon solar panels, a solar panel. Technically, this is related to the previously described thin film solar cell. They fall under the same category of “thin-film” solar cells despite minor variances in their production.
Furthermore, the amorphous silicon solar cell is made at a meager cost, much like the previously described thin film solar cell.
Even though amorphous silicon solar panels have an efficiency limit of 7%, buying multiple of them is frequently more cost-effective. It’s crucial to have cheap solar panel manufacturing capabilities.
Additionally, this technology must be available to consumers at affordable pricing. Amorphous silicon solar cells and panels are among the most significant solar panels available because of this.
5. Passivated Emitter and Rear Cell (PERC) Solar Panels
Passivated Emitter and Rear Cell (PERC) Solar Panels are other solar panels. PERC solar panels, also called “rear cells,” are created utilizing cutting-edge technology.
The solar cells’ backs are covered with a coating to accomplish this. Traditional solar panels only partially absorb sunlight; some of it flows through them.
The PERC panels’ extra layer enables sunlight that hasn’t been fully absorbed to be reabsorbed from the back of the panels, increasing efficiency.
Nowadays, high-efficiency Mono-PERC panels with the greatest power ratings among commercially available solar panels are created by commonly combining PERC technology with monocrystalline cells.